Summary
R14 Alkaline battery is too powerful for a month life. No merit to use R6 Mn battery. XBee may be less than 10 times to reuse deteriorated NiCd or NiMH batteries unavailable to run GE A1455 digital camera. TWE seems to be longer battery life than XBee because of little peak current consumption.
Motive
Evaluate battery life for TWE or XBee wireless module in field test.
要約
電池寿命の目途を1箇月程度とみなすと,R14 サイズのアルカリ電池は不要である。R6サイズのMn電池使用のメリットはない。GE A1455 デジカメを 起動しなくなった劣化 NiCd と NiMH の再利用はおそらく10回未満の使用に限られる。電池ブランドにより電池寿命に差異が認められた。
経緯目的
XBee を用いたワイヤレス温度センサのフィールド試験を行い電池寿命を求める。トップページからの再掲記事です。
Battery life field test results 電池寿命フィールド試験結果
| Type | Work temp | Size | Retail price | Result days | Module |
| Mn | - | R6 | ¥108/8pc Daiso | 77/72, 60/64 | XBee |
| Mn | - | R14 | ¥108/2pc Daiso Daiso & Pana Pana Pana & Moritoku ¥108/3pc Moritoku | 122, 185, 214 97, 80 81 80 130, 170 | XBee |
| Alkaline | 5 to 45°C | R6 | ¥108/5pc Daiso | 166, 190, 361#2, 201#2 | XBee |
| Alkaline | 5 to 45°C | R14 | ¥108/pc Daiso | - | - |
| NiMH | 0 to 50°C | R6 | ¥480/2pc 2000mAh Impulse Deteriorated 950mAh Eneloop Deteriorated 1000mAh Evolta Deteriorated Evolta & 1300mAh ReVoltes | 83 34#2 106#6 85, 45, 14, 51 134#5, 136#5 54 156#4, 180#4 | XBee TWE XBee TWE XBee TWE |
| NiCd | -20 to 60°C | R6 | Deteriorated 1000mAh GP Deteriorated GP & Eneloop | 42, 35, 28, 22 54#5, 70#4, 61#4, 96#4, 90#6 136#5, 163#6 | XBee TWE |
| Li | -20 to 60°C | R6 | ¥613/4pc Yodobashi | - | - |
Battery choice 電池選択に際して
The standard JISC of Alkaline battery is constant current load, while Mn battery is constant resistor load only. We cannot compare them simply. Panasonic old catalog depicts continuous constant current load characteristics, so we can compare them. In the cases of R6 batteries, Mn and Alkaline read 7h and 20h each. The capacity are 700mAh and 2000mAh equivalent. The discharge ratio is 2.9 folds therefore.
NiMH discharge standard is also different from alkaline battery. The duty of an hour in day is the longest life. 0.2C current discharge time of 5 hours at 20℃ decreases to 2 hours at 0℃. The remarkable definition of cycle life is the number of cycles to decrease to discharging 2 hours through initial 5 hours at 0.2C rate. For example, the life cycles allow that 1000mAh decrease to 600mAh.
I have used deteriorated NiCd batteries, but they are not on sale now. Tbl.1 shows the result of field test.
My TWE modules adopt I2C sensor, so the power supply need not regulate sensor power supply, as DC/DC converter supplies power. TWE sensors are driven by deteriorated NiMH batteries, and XBee sensors are driven by alkaline batteries.
#5 stopped at 2.38V, though my tiny voltage regulator works #5 at 2.2V. NiMH internal resistance may be big. I think that #5 stopped because minimum working voltage of TSL2561 is 2.7V nominal.
Wireless module of #1 is XBee. I tried 3 battery brands of Daiso, Panasonic and Moritoku. It seems that the battery life depends on the brands.
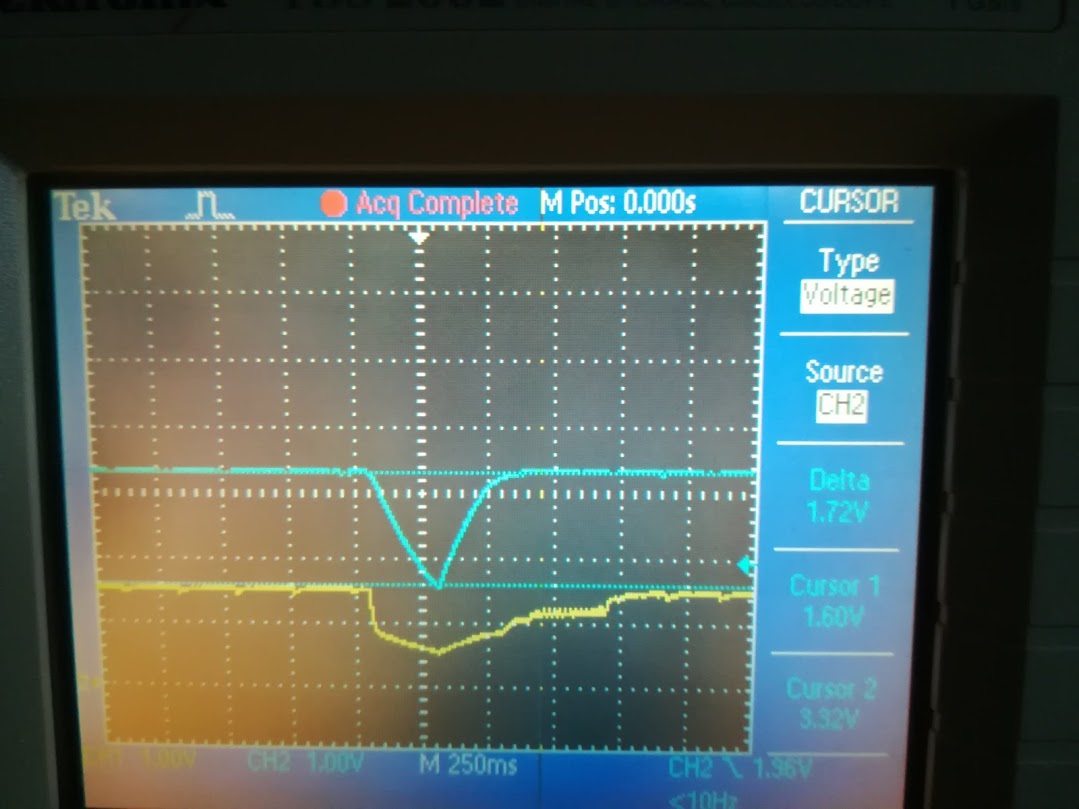
Figure 13 shows dissipated R14 Mn battteries voltage sag while XBee transmitting. The sag measured by DSO. CH1 (yellow) and CH2 (blue) are 1V/div, 250ms/div. CH1 3V3 drops 1.72V which is less than the minimum voltage that XBee works. Then CH2 batteries voltage drops less than the minimum volatage that DC/DC converter works.
JISC では,アルカリ乾電池には定電流負荷の規格がある一方,マンガン電池の放電規格は固定抵抗負荷のみであるから,単純に両者の放電性能を比較できません。 Panasonic の古いカタログにマンガン電池の連続定電流特性が記載されているので両者の放電性能を比較できます。単3電池 100mA 連続定電流負荷の場合,マンガンとアルカリは7h,20hと読み取れ,容量は それぞれ700mAh と 2000mAh に相当します。したがって放電性能比は 2.9 倍になります。
ニッケル水素電池の放電性能もアルカリ電池の試験仕様と異なります。 アルカリ電池の最も寿命が長くなる放電時間は1日に1時間(100mA)のデューティです。ニッケル水素電池だと,放電電流 0.2C において20℃だと5時間の放電時間が,0℃だと2時間に低減する規格になっています。
これまで,劣化したと思われる NiCd 電池を使用してきましたが,もう量販店では流通していないようです。Tbl.1 に現在入手が容易な電池とその屋外使用試験結果を示します。ニッケル水素電池のサイクル数に ついて注意が必要です。0.2C の放電電流において放電時間5時間が3時間未満になるまでのサイクル数の事です。例えば初期 1000mAh の容量が 600mAh までの低下を許容した回数になります。
Panasonic 製Mn電池による寿命が Daiso + Panasonic 混合組み合わせより16日間短くなりました。電源電圧は 3V3 が得られています。個別の電圧は 1.19V と 1.18V でした。しかし,DSO で 電圧を測定すると変動が見られ電圧降下サグが観測されました。周期は 20.8s でした。ポーリング周期と一致しています。電源電圧が 2.1V 以下となる時間は 140ms でした。この電圧低下が通信不能に 至ったのでしょう。Daiso 純正,Daiso+Panasonic さらに Panasonic のみと電池ブランドが変わると,電池寿命が低下しています。Daiso 取扱の Panasonic はパルス負荷を持続すると内部抵抗が 大になり電圧低下を招くのかもしれません。ネット情報では富士通マクセルの性能が良さそうですが,近在の百均ショップではもう見受けられません。百均ショップ Meets ではモリトクの 3本入りがあり,Panasonic と混同使用しました。モリトクは Daiso と同程度の寿命が得られました。
Figure 13 に R14 のマンガン電池が消耗して XBee が送信不能になった際の電源電圧サグとバッテリ電圧の変動の様子を示します。測定は DSO を用い,CH1 (yellow) 3V3 と CH2 (blue) バッテリ電圧はそれぞれ 1V/div, 250ms/div です。送信時,電源電圧が低下して2Vを下回っており 送信不能となっています。バッテリ電圧も 1.5V から 520mV 低下しています。
マンガン R14 の寿命はアルカリ LR6 とほぼ同等です。電池単価と占めるスペースを考慮すると,R14 のコストパフォーマンスは良くありません。 マンガン R14 を使用するメリットは余りなさそうです。
Ambient temperature effect 温度による影響
Panasonic publicizes battery temperature characteristics. Mn battery can discharge for 7 hours at constant current load and 20℃. The discharge time decreases to 5.5 hours at 0℃. The decreased raito is 20% equivalent.[10]
Whether to use one-time or rechargeable battery, its decision is of ambient temperature and control of the batteries history. My XBee applied sensors monitor battery voltage, and may not be over discharge. The test results are actual batteries life in field test. It seems that the battery life changes in seasons, but the result is not the same of Panasonic Mn temperature characteristics. One is continuous current load, the other is pulse load. The battery itself is not Panasonic but Daiso. Ambient temperature always varies in field test, while Panasonic temperature characteristics is constant temperature. It is certain that varying temperature in seasons effects battery life.
Li battery has good performance at low ambient temperature, but it is necessary to add power supply circuit.[9]
Panasonic が電池の温度特性を公開しています。マンガン電池 100mA の定電流負荷において20℃の場合,7時間放電します。温度特性図の7時間と20℃のグラフが交差した抵抗値を求め,下方に移動して0℃の 交点を求めると,およそ 5.5 時間を得ます。これは 20% の減少に相当します。[10]
使い捨ての乾電池を使うか,もしくは充電池にするのかを選択する判断基準は使用温度と充電池を適切に管理できるかです。本センサは電池電圧をモニタしているため, 充電池の過放電を避けられます。また電池切れ直前の電池交換も可能になります。試験結果は屋外フィールド試験を行った実際の電池寿命です。季節による温度変化により電池寿命も 変るようにみえますが,Panasonic が公表しているマンガン電池の温度特性とは一致しません。連続電流負荷とパルス負荷,電池本体も Panasonic と Daiso と異なります。実際のフィールド試験では温度は 絶えず変動する一方,Panasonic の公表温度特性は一定温度と違いがあります。季節による温度変動が電池寿命に影響を及ぼしているのは確かなようです。
Li 乾電池の低温度特性が優れている。長期の零下環境下ではいいかもしれないが,公称電圧 1.8V なので電源回路が必要になります。[9]
Ref 引用
[9] リチウム乾電池[10] マンガン乾電池
Which is better NiCd or NiMH? NiCd と NiMH のどちらを選択するか
I compared NiCd with NiMH about ambient temperature effect of discharging capacity. Reading Figure 12 and data sheet distributed by Akizuki Denshi, I listed table 2.[11][12]
NiCd may be more durable than NiMH at extreme high or below ambient temperature. For example, NiCd is better in Hokkaido Japan, Canada or Manchuria. But one coin shops do not sell NiCd batteries now. And more, the both batteries work to operate within 0 to 35°C on artificial satellites.[13]
Ref.
[11] 単3型 NiCd 充電池 GP100AAKC 1060mAh[12] ニッケル水素電池カタログ
[13] Development of Li Ion Cells for Satellite Applications
| Temperature | NiCd | NiMH |
| 60°C | 105 | - |
| 45°C | 105 | 96 |
| 20°C | 100 | 100 |
| 0°C | 95 | 89 |
| -10°C | 90 | 80 |
| -20°C | 80 | - |
Double shade effect 二重笠効果
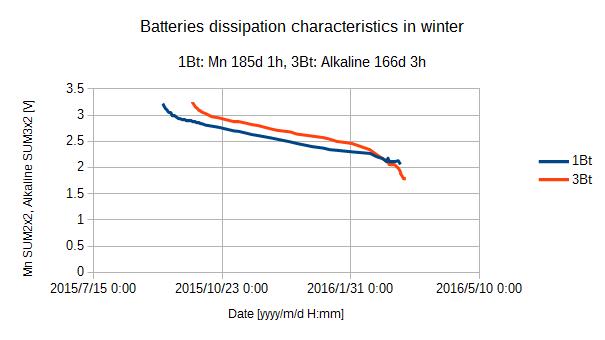
Fig.5 にアルカリ R6(単3) とマンガン R14(単2) を用いた秋から春にかけての電池寿命結果を示します。これまでのマンガンとアルカリを比較すると,寿命が倍以上延びています。 5℃以下になると,R14 のマンガン電池の出力はアルカリに比べ,出力が低下した結果が得られています。0℃まで下がるような環境ではマンガン電池は不利なようです。
ワイヤレス温度センサは間欠的に動作し,待機電流は極めて少ないですが,データ送信時には 100mA 程度のピーク電流が必要となります。ピーク負荷に対してもアルカリ電池は マンガン電池より優れており,R6に関してはマンガン電池を採用するメリットはないようです。
R14 マンガン電池寿命が前回と比べ,大きく伸びています。動作停止電池電圧が上昇しているものの高温に曝されないため放電期間が延びたのでしょうか。よくわかりません。 これもフィールド試験から得られた知見です。その後 2016-03-19 に電池を交換した #01 機は 3.20V からスタートし,10-19 に 1.43V に至り電池を交換しました。214日間の寿命となりました。 太陽輻射熱を避ける二重笠が電池の寿命を伸ばしているようです。
Fig.5 shows a battery life of Alkaline R6 and Mn R14 in fall throungh spring. Alkaline battery life is more than Mn twice. R14 Mn battery did not work as well alkalin below 5℃. Mn battery seems not to be good below 0℃.
Wireless temperature sensor wakes at instant and sleeps. Though the waiting current is negligible, 100mA dissipates at peak when transmitting data. It seems that Mn battery works worse than alkaline at peak load. You might not use R6 Mn battery.
R14 Mn battery life is much longer than before. I do not know why discharging time is longer in low ambient temperature with getting higher terminal discharging voltage. #01 started at 3.20V 2016-03-19. I replaced batteries 2016-10-19 at 1.43V. It worked for 214 days. The double shade seems to decrease the sun radiation heat and it might be longer life.
デジカメを起動しなくなった劣化充電池の再利用
2016 年6月新たに Daiso LR6 電池消耗データが得られました。最近の円安のせいか乾電池の価格が上昇しています。Daiso は LR14 価格を倍に改定しました。同年8月 NiMH の実測データが得られました。 アルカリ電池と比較すると半分の寿命になっています。NiMH はデジカメ GE A1455 に使用し,4回充放電させています。自己放電が大きく間欠動作のミリ秒 ms 単位微小パルス負荷に不向きなのか, それとも満充電になっていなかったのかもしれません。一方,2000mAh の容量表示は JISC 8708 密閉形ニッケル・水素蓄電池の試験要領によれば,容量ではなく回数だとわかります[3]。 0.25It の電流が極端な話,1分未満の放電でも1回として加算されてしまう内容です。50回単位です。従来の C とは異なる概念と思っていいのではないでしょうか。
ゲーム機のワイヤレスコントローラとして使用に耐えなくなった NiCd と Evolta をワイヤレスセンサの電源として使いまわしています。使い古した NiCd はデジカメにも使用できていますが, Evolta は劣化が酷くデジカメを起動できません。NiCd は劣化していても,新品のアルカリ電池よりも大ピーク電流を取り出せるのでカメラを起動させられます。8月28日にワイヤレスセンサに適用したところ, 42日間の寿命となりました。電源電池電圧が 2.01V からたった45分間の間に 1.03V まで低下しました。片方の電池電圧を DMM で計ると零ボルトでした。電池個体間の劣化程度およびバラツキを管理しない事には 寿命を伸ばすのは困難でしょう。Panasonic は使いまわしと電池の組み換えを電池寿命の観点からしないようにと説明しています。今は 4000 カウントの DMM が安く入手できるので,高精度に電池電圧が計れます。 通常型潜水艦乗組員のように充電池組み換えもいいかなと思います。Panasonic が推奨するような使い方だと電池数が増えてしまいますし,まだ他の用途に使えるのに廃棄するのはムダというか, 経済的ではありません。
手間をかけたくなければ,使い捨て電池がいいかと思います。
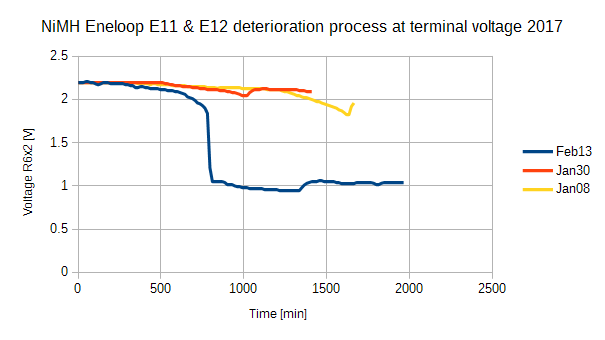
Figure 8 に劣化 Eneloop の電池交換例を示します。NiMH を 1.0V 以下まで放電させると過放電となり寿命が短くなります。交換時の装荷状態での電池単体電圧はそれぞれ 1.03V と 0.942V でした。 記録周期までに電池を交換すれば,測定データの欠損は生じません。交換後の電池はつい最近デジカメを起動できなくなった NiCd です。
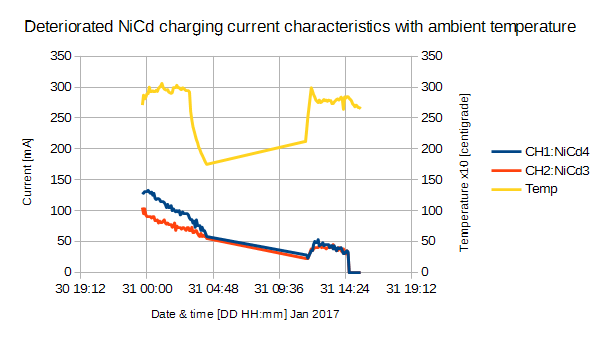
劣化 Evolta が冬期間において54日の寿命を得ました 2017-01-15。 デジカメのようなピーク負荷には適用できないものの XBee の駆動には十分だと思います。その後,NiCd の劣化進行状況がわかるデータが 得られたので公開します。Figure9 に劣化 NiCd の自製充電記録器による充電流変化を示します。この NiCd を室内に設置した#3に使用後,再充電した結果が Figure10 です。本充電器は定電流駆動と定電圧駆動を 併用しています。充電初期は設定した定電流 200mA が支配的です。自製記録器はマイコンによるもので電流値はピーク値です。DSO による平均値だと 200mA です。劣化が進んだのか,Figure10 の初期電流は 設定電流値 200mA に達していません。充放電停止電圧が上昇したため低い充電流にとどまったと思われます。
充電終了を知らせる機能がある充電器だと,ある程度の充電池劣化の見極めが可能でしょう。ただし,安価品はタイマで知らせるものがありますので注意が必要です。 #3の測定期間が22日と1箇月未満に低下したので,今後 XBee への長期運転使用を止めます。Figure10 にある直線部チャートはPCの USB ポートの電源不調によるものと思われます。マイコンの電源は USB から給電しています。Figure11 に同じ NiMH Eneloop 充電池のペアによる終末電圧低下の様子を 2.2V からチャートにしました。直近の場合だと装荷状態での個別末期電圧が,0.152V と0Vでした。
参照 Ref
- JISC8500 一次電池通則
- JISC8515 一次電池個別製品仕様
- JISC8708 密閉形ニッケル・水素蓄電池
- Panasonic 電池データ
- NiMH 定電圧解放または電圧カットオフ
- 新たな用途展開を図るニッケル水素電池の新技術
Reuse deteriorated NiCd and NiMH not to run digital camera
I got Daiso LR6 dissipation data in June 2016. I got NiMH data in August. The NiMH life is half of Alkaline. The NiMH was for GE A1455 digital camera. I discharged and charged four times. Is self discharge big or unsuitable for mili second pulse load? Or it did not charge full.
I reuse NiMH Eneloop and Evolta that cannot use for wireless game controller. Deteriorated GP NiCd and Eneloop NiMH can run the camera, but NiMH Evolta ones cannot run. Deteriorated NiCd can discharge peak current than new alkaline batteries. The NiCd batteries started on August 28. They worked for 42 days. It took only 45 minutes to drop down 1.03V at higher 2.01V. One of both batteries measured 0V by DMM. It is difficult to enlarge battery life without controlling individual deterioration. Panasonic recommends not to reuse and change pair of batteries. We can buy 4000 count DMM at low price now. So we can measure battery voltage at high accuracy. The crews of usual battery driven submarines change pairs of batteries. Panasonic recommendation increase stock of batteries. Throwing away, it is not economical to be able to reuse ones, I think.
You may choose primary batteries without extra routine.
If you use NiMH battery below 1.0V, the life will shorten. I show an example of battery replacement within recording period in Figure 8. I measured the pair of batteries each by DMM. They are 1.03V and 0.942V. The replaced deteriorated batteries are NiCd that have not been able to run GE digital camera.
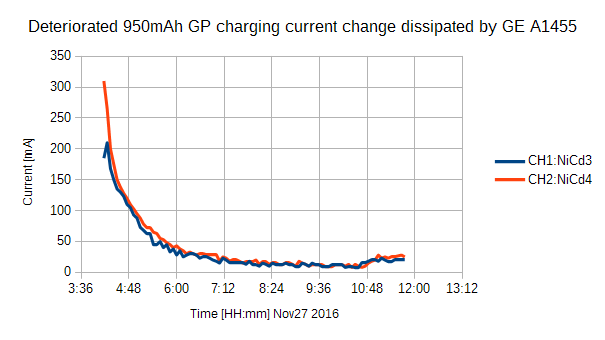
Deteriorated 1000mAh Evolta duration is 54-day in winter 2017-01-15, though their peak load available are poor. They could drive XBee. I have made a charger by constant current drive and constant voltage drive. Figure9 shows deteriorated NiCd charging current that AVR and PC recorded. The batteries was dissipated by #3 wireless sensor and the life was 22-day only less than a month. I charged them and the charging currents have been in Figure 10. The current were less than constant current 200 mA. It shows that deteriorated batteries decrease initial current because of deterioration. If you have a charger that shows the status of full charging, you will find the battery deteriorated. But a cheap charger showing full up by timer is not for deterioration criteria.
Figure 9 and 10 were recorded by my scratch AVR and USB serial converter. My program does not have mean processing by programming. DSO measurement shows 200mA mean each. The line part of chart in Figure 10 seems of my poor USB port of my PC that cannot feed current enough for a long time. The other port can feed full.
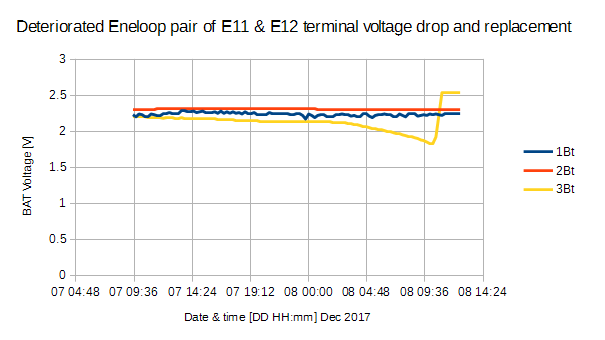
Figure 11 shows that terminal voltage drop of the same pair of NiMH Eneloop E11 and E12 from 2.2V three times. You will find them deteriorated step by step. If you plot terminal voltage drop like these, you will be able to find NiMH deterioration.
Mix of deteriorated NiMH and NiCd 劣化 NiMH と NiCd の混用
Deteriorated Eneloop 11 and NiCd3 worked TWE #6 for 163 day till 2018-09-20. I measured 1.288V of Eneloop and 0.809V of NiCd just before removing the batteries on 09-21. #6 has increased the transmitting interval to 3 minutes since 2018-04-10.
09:45 1.15V
09:30 1.72V
09:15 2.14V
09:00 2.21V
08:45 2.23V
The battery life was only 12 days. I will not reuse NiCd1 for wireless sensor.
While deteriorated NiCd6 and Eneloop11 has worked #5 for 136 days. Its illuminance sensor stopped at 2.39V.
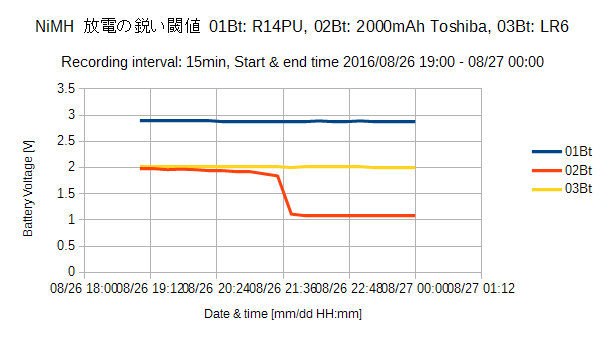
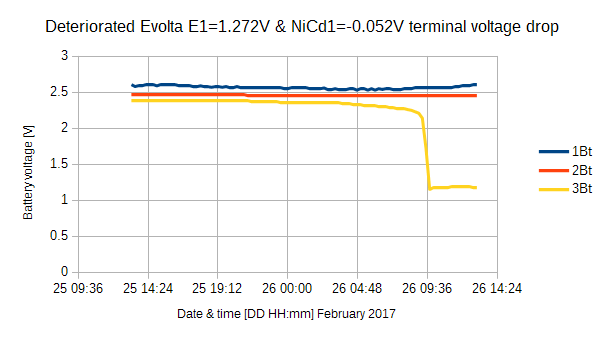
劣化した NiMH 1000mAh Evolta E1 と NiCd 1000mAh GP NiCd1 を#3に装荷しました。バッテリ電圧は2月26日 9:45 に急落しました。その日の午後, MM PC510 で各電圧を装荷状態で計ったら, -0.052V (NiCd) と 1.272V (NiMH) でした。直近1時間の電圧は左に示すように減少しました。その寿命は12日に 過ぎません。
Actual terminal battery voltage limited by sensor device or DC/DC 終止電圧と律則デバイス
| ID | Terminal date | Terminal voltage [V] | Device | BAT | Interval [min] | Duration [day] |
| #3 | 17-01-30T18:30 | 2.09 | DC/DC | NiCd3 NiCd4 | 1 | 22 |
| #3 | 17-02-13T22:00 | 1.04 | DC/DC | Eneloop 21 22 | 1 | 14 |
| #3 | 17-02-26T13:45 | 1.17 | DC/DC | NiCd1 Evolta1 | 1 | 12 |
| #2 | 17-01-15T17:30 | 2.00 | DC/DC | Evolta | 1 | 54 |
| #2 | 17-03-08T14:00 | - | DC/DC | Eneloop 11 12 | 1 | 51 |
| #2 | 18-10-02T08:00 | 1.87 | DC/DC | LR6 Daiso | 3 | 201 |
| #2 | 18-11-06T20:00 | 2.40 | DC/DC | Impulse | 3 | 34 |
| #1 | 17-01-15T8:45 | 2.25 | DC/DC | R14 Daiso Panasonic | 1 | 97 |
| #1 | 17-04-08T09:45 | 2.24 | DC/DC | R14 Panasonic | 1 | 81 |
| #1 | 17-11-08T01:15 | 2.23 | DC/DC | R14 Moritoku | 1 | 130 |
| #1 | 18-04-30T13:00 | 1.53 | DC/DC | R14 Moritoku | 1 | 170 |
| #4 | - | 2.28 | ADT7410 | NiCd2 NiCd6 | 1 | 96 |
| #4 | 18-03-05T11:30 | 2.30 | ADT7410 | Evolta ReVoltes | 1 | 156 |
| #4 | 18-03-26T01:00 | - | ADT7410 | NiCd3 NiCd5 | 1 | 19 |
| #4 | 18-09-23T18:15 | 2.27 | ADT7410 | ReVoltes Evolta | 1 | 180 |
| #5 | - | 2.38 | TSL2561 | Eneloop 21 22 | 1 | 134 |
| #5 | 18-03-23T02:30 | 2.39 | TSL2561 | Eneloop11 NiCd6 | 1 | 136 |
| #5 | 18-08-17T18:45 | 2.35 | TSL2561 | Eneloop 21 22 | 3 | 142 |
| #6 | 17-12-23T20:45 | 2.46 | SHT21 | NiCd3 NiCd5 | 1 | 90 |
| #6 | 18-04-07T16:00 | 2.54 | SHT21 | Impulse | 1 | 106 |
| #6 | 18-09-20T13:15 | 2.32 | SHT21 | NiCd3 Eneloop11 | 3 | 163 |
機番#1 #2 および #3 のワイヤレスモジュールは XBee であり,センサを駆動するために DC/DC で電源電圧を 3V3 にポンプアップしている。DC/DC そのものは 0.8V 以上で動作するが,ピーク電流が 100 mA を超えるせいもあり,電池自体の終止電圧が律則のようです。
機番#4 #5 および #6 のワイヤレスモジュールは TWE です。DC/DC を搭載していません。
温度センサ,照度センサおよび温湿度センサはそれぞれ 2.3V 2.4V 2.6V以下になると,動作しなくなるようです。公称値より小さい値になっています。
また劣化 NiCd3 と Eneloop11 の混載は TWE #6を 163 日間駆動しました。
電池寿命を延ばすために送信間隔を1分から3分に延長しています。寿命が3倍になるというわけでもなさそうです。
#2 XBee で使用した Impulse が放電停止電圧 2.40V と高くなっています。DC/DC の下限動作電圧は 0.7V だから,劣化充電池は DC/DC 非搭載の TWE 専用にした方が良さそうです。
© Enoki 2018 updated October 4